Unlocking the Power of Social-Emotional Learning for Youth Mental Health
In a world where young minds face unprecedented pressures and challenges, nurturing their mental health and emotional well-being is paramount. The facts are startling. We hope to shed light on the reality of the problem, and offer solutions and provide community resources to combat this pervasive and complex issue.
October is a month with several dedications to promoting Mental Health Awareness; it is a time to acknowledge the significance of mental health and explore effective strategies for supporting our youth. One such strategy that has gained remarkable recognition in recent years is Social-Emotional Learning (SEL).
Have you heard of it?
It isn't just a buzzword
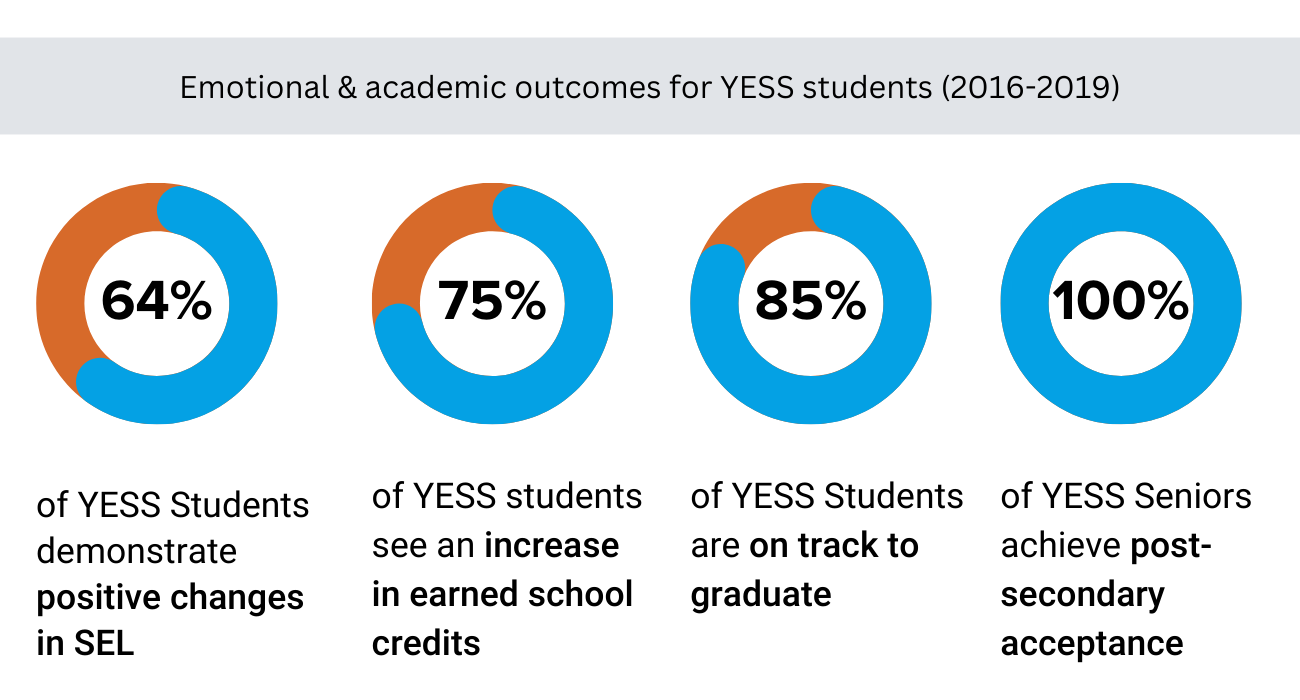
Social-Emotional Learning is more than just a buzzword; it's a transformative approach that has the potential to revolutionize the way we support youth mental health. SEL programs - such as those offered by the YESS Institute - have demonstrated impacts on student outcomes both behaviorally and academically.
YESS SEL programs impacted it's students between 2016-2019:
The Youth Mental Health Crisis
What do you know about youth mental health?
Fact 1: According to the National Institute of Mental Health, approximately one in five youth in the United States experiences a severe mental disorder in their lifetime. These issues can include anxiety, depression, and behavioral disorders, among others[1].
The Role of Social-Emotional Learning (SEL)
In our current bio-social landscape of increasing mental health challenges, Social-Emotional Learning (SEL) emerges as a beacon of hope. SEL programs are designed to equip students with the necessary skills to understand and manage their emotions, build healthy relationships, and make responsible decisions. By integrating SEL into the educational curriculum, we offer young individuals a toolkit to navigate life's complexities.
Empowering Youth through SEL
The power of SEL lies in its ability to provide young minds with essential life skills, which are not only invaluable for academic success but also for maintaining emotional resilience in the face of adversity.
Ready to empower youth through SEL? Discover how YESS Institute's programs can make a difference.
Beyond the Classroom: SEL and Academic Success
Fact 6: SEL enhances student engagement. A report by CASEL (Collaborative for Academic, Social, and Emotional Learning) found that schools implementing SEL programs saw improved classroom behavior and attitudes towards school, leading to better overall academic performance[6].
Supporting Youth Mental Health: Resources for All
As we conclude our exploration of the profound impact of Social-Emotional Learning on youth mental health, we want to provide you with valuable resources to further this critical conversation.
Colorado Behavioral Health Administration is a hub for many mental health resources in Colorado, for both youth and adults. Explore their website to learn more about the available programs.
Connect with YESS today to learn how we can bring Social-Emotional Learning programs to your community.

References

-
1385 S. Colorado Blvd 610-A
Denver, CO 80222 -
303-709-8178