Cannabis-use & brain development
The use of the Cannabis plant (also commonly referred to as marijuana), has been a hotly debated topic in recent years. Despite some claiming that cannabis is a completely harmless recreational drug, research has revealed that its use can have long-term effects on brain development, particularly in adolescence. This article explores the impact of adolescent cannabis-use on brain development.
Youth drug awareness & education is critical
Located in Colorado, the first state in the US to legalize recreational Cannabis-use, the YESS Academy acknowledges the importance of sensible youth Cannabis education. Research has shown that effective adolescent Cannabis education should be context-specific, with programming tailored to the unique realities of each school or program. Youth drug awareness and education efforts are more critical than ever, given the alarming statistics on youth drug abuse at the state and national levels.
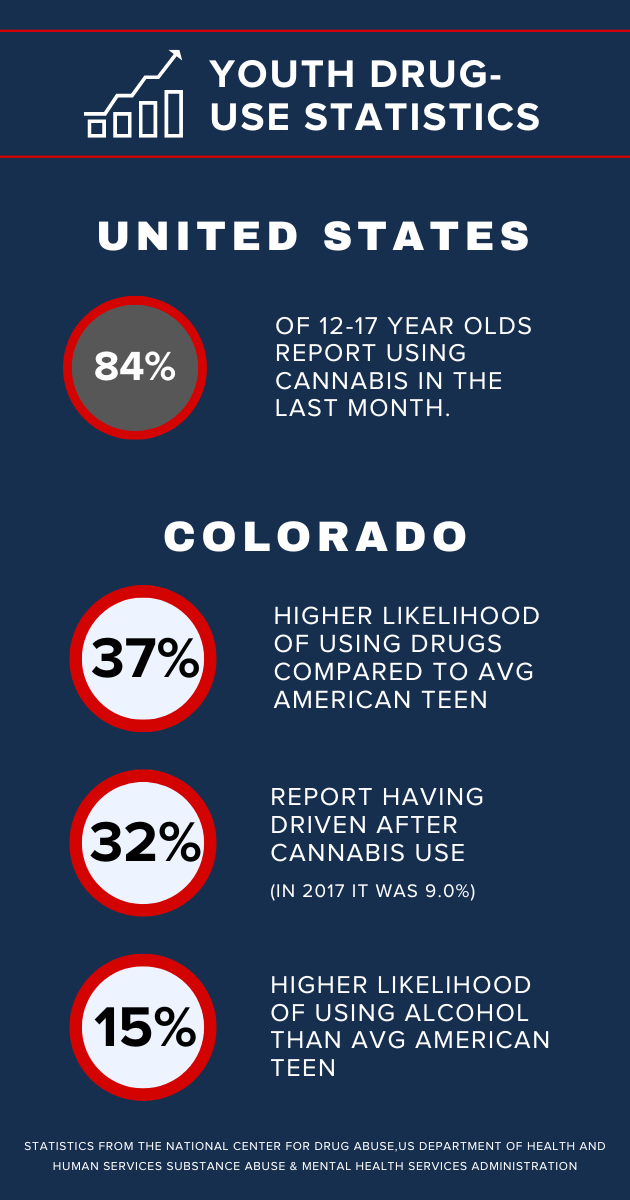
<- Check out the statistics on youth drug use for individuals ages of 12-17 years in the US and in Colorado
<- Check out the statistics on youth drug use for individuals ages of 12-17 years in the US and in Colorado
See References 1-4 for full details related to youth drug use statistics in the United States and Colorado.
Risks regarding brain developement
Studies indicate that Cannabis-use during adolescence can have negative effects on the development of the prefrontal cortex, which can result in issues with attention, memory, and decision-making. This can have serious, long-term consequences for academic and career success, relationships, and overall quality of life. Individuals who start using cannabis before the age of 16 have been shown to have lower IQ scores and poorer cognitive function than non-users.
Furthermore, regular Cannabis-use during adolescence is associated with an increased risk of mental health issues such as depression and anxiety. Addiction is another concern, as research has demonstrated that the earlier an individual starts using cannabis, the more likely they are to become addicted, with potential consequences such as impaired judgment, instability, and financial problems.
Furthermore, regular Cannabis-use during adolescence is associated with an increased risk of mental health issues such as depression and anxiety. Addiction is another concern, as research has demonstrated that the earlier an individual starts using cannabis, the more likely they are to become addicted, with potential consequences such as impaired judgment, instability, and financial problems.
Addiction
It is essential to note that the impact of Cannabis on the brain is not limited to adolescence, it just looks different in adults. Regular heavy Cannabis-use during adulthood can lead to changes in brain structure and function, particularly in areas related to memory and learning, often presenting in short-term symptoms. Thus, Cannabis education and awareness should continue beyond adolescence to help prevent potential negative consequences associated with Cannabis-use. In general, if Cannabis is available as a recreational drug, so too should ample age-appropriate and publicly accessible resources and education opportunities.
Let us know your favorite educational resources in the comments below!
Let us know your favorite educational resources in the comments below!
Empty space, drag to resize
YESS Academy is the product of collaboration between YESS Institute, RadSchools, and Denver Afterschool Alliance. We are grateful to our many community supporters and participants who have helped make our resources streamlined, effective, and available to you in multiple modalities.
Empty space, drag to resize
References
1. National Center for Drug Abuse Statistics. 2022. https://drugabusestatistics.org/teen-drug-use/
2. Anne E. Casey Foundation. Kids Count Data Center. https://datacenter.kidscount.org/data/tables/101-child-population-by-age-group#detailed/1/any/false/1729/64,6/419,420
3. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (DHS) Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA), National Surveys on Drug Use and Health. National Surveys on Drug Use and Health: 2018-2019. https://www.samhsa.gov/data/sites/default/files/reports/rpt32879/NSDUHsaeTotal2019/2019NSDUHsaeTotal.pdf
4. Colorado Substance Abuse Trend and Response Task Force. Annual Report. 2021. https://coag.gov/app/uploads/2020/12/2021-Annual-Report-Substance-Abuse-Trend-Response-Task-Force.pdf
5. Center for disease control and Preventtion: https://www.cdc.gov/marijuana/health-effects/brain-health.htm
1. National Center for Drug Abuse Statistics. 2022. https://drugabusestatistics.org/teen-drug-use/
2. Anne E. Casey Foundation. Kids Count Data Center. https://datacenter.kidscount.org/data/tables/101-child-population-by-age-group#detailed/1/any/false/1729/64,6/419,420
3. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (DHS) Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA), National Surveys on Drug Use and Health. National Surveys on Drug Use and Health: 2018-2019. https://www.samhsa.gov/data/sites/default/files/reports/rpt32879/NSDUHsaeTotal2019/2019NSDUHsaeTotal.pdf
4. Colorado Substance Abuse Trend and Response Task Force. Annual Report. 2021. https://coag.gov/app/uploads/2020/12/2021-Annual-Report-Substance-Abuse-Trend-Response-Task-Force.pdf
5. Center for disease control and Preventtion: https://www.cdc.gov/marijuana/health-effects/brain-health.htm

-
1385 S. Colorado Blvd 610-A
Denver, CO 80222 -
303-709-8178
Youth drug awareness/education that works.